The problem of detecting loops in a linked list is an important algorithmic problem in computer science. A linked list is a popular data structure used to store a collection of elements, where each element points to the next one in the list. A loop occurs in a linked list when there is a cycle of elements that forms a loop, rather than a linear sequence.
Detecting loops in a linked list is an important problem because it can help us identify potential bugs or issues in our code, such as infinite loops or unintended behaviour. In addition, many common operations on linked lists, such as reversing or sorting, can be more complicated or impossible to perform if the list contains a loop.
One common approach to detecting loops in a linked list is to use the “tortoise and hare” algorithm, also known as Floyd’s cycle-finding algorithm. This algorithm uses two pointers that traverse the linked list at different speeds, and if there is a loop in the list, the two pointers will eventually meet at the same node. By using this algorithm, we can efficiently detect whether a linked list contains a loop without requiring any additional data structures or using excessive memory.
Okay but what is a Loop in a Linked List Exactly?
A loop in a linked list occurs when there is a cycle of nodes that forms a loop, rather than a linear sequence. In other words, there is a node in the list that is reachable from more than one other node in the list, forming a cycle.
For example, consider the following linked list:
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3 -> ...In this linked list, the node with the value 2 is reachable from two other nodes (1 and 4)
1 -> (2) -> 3 -> 4 -> (2) -> 3 -> …
And the node with the value 3 is also reachable from two other nodes (2 and 4).
1 -> 2 -> (3) -> 4 -> 2 -> (3) -> …
This creates a cycle in the list, and the list is said to contain a loop…
This cycle causes the linked list to loop back on itself, rather than continuing in a linear sequence. Loops in linked lists can cause various issues and unexpected behaviour, so it is important to be able to detect and handle them when working with linked lists in software development.
How to check the Linked List contains a Loop?
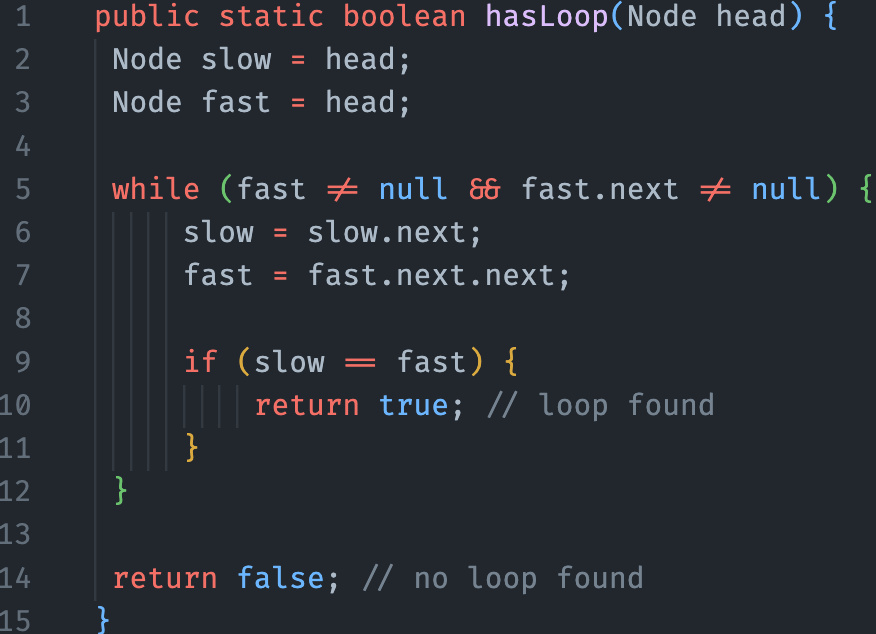
Let’s demonstrate the “Floyd’s cycle-finding algorithm”, also known as the “tortoise and hare algorithm”.
This algorithm uses two pointers to traverse the linked list at different speeds, and if there is a loop in the list, the two pointers will eventually meet at the same node.
- Start with two pointers,
slowandfast, both pointing to the head of the linked list. - Move
slowone node at a time andfasttwo nodes at a time. - If the
fastpointer reaches the end of the list (i.e., becomesnull), then there is no loop in the list and we can returnfalse. - If the
fastpointer meets theslowpointer (i.e.,fast==slow), then there is a loop in the list and we can returntrue.
This algorithm is based on the idea that if there is a loop in the linked list, the fast pointer will eventually “lap” the slow pointer and they will meet at the same node.
By iterating over the linked list using two pointers at different speeds, we can efficiently detect whether a loop exists in the list without requiring any additional data structures or using excessive memory!
public static boolean hasLoop(Node head) {
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true; // loop found
}
}
return false; // no loop found
}Final Note
Understanding whether there is a loop in a linked list is important because it can help prevent issues and unintended behaviour in software development.
Loops in linked lists can cause various problems, such as infinite loops or incorrect results from common operations like reversing or sorting the list. If a linked list contains a loop, algorithms that traverse the list can get stuck in an infinite loop, which can crash the program or cause other issues. In addition, loops can cause incorrect results from search or sort algorithms that assume the list is a linear sequence.
📚 Further Reading & Related Topics
If you’re exploring linked lists and algorithmic problem-solving in Java, these related articles will provide additional insights:
• Difference Between TreeSet and TreeMap in Java – Understand how Java’s TreeSet and TreeMap handle sorted data structures, which can be useful for efficiently managing ordered collections.
• Java Streams: Unleashing the Power of Functional Programming – Learn how Java Streams can simplify operations on collections, including filtering and detecting patterns in data structures like linked lists.








Leave a comment