Greetings, dear devs again! Today, we’ll explore the fascinating world of Java Streams in combination with Java Persistence API (JPA) to create powerful, efficient, and expressive data processing solutions. Java Streams enable us to harness the power of functional programming, while JPA provides a standardised way to interact with relational databases. So let’s embark on this exciting journey and discover how Java Streams and JPA can help us build more elegant and efficient data processing solutions!
Understanding Java Streams and JPA
Java Streams, introduced in Java 8, provide a functional-style API for processing collections of data, such as filtering, mapping, and reducing. JPA, on the other hand, is a standard API for managing relational data in Java applications. By combining Java Streams and JPA, we can create powerful solutions for processing and manipulating data stored in relational databases.
Using Java Streams with JPA
Let’s explore some common use cases for Java Streams with JPA. In the following examples, we’ll assume that we have a simple Person entity and a PersonRepository that extends JpaRepository.
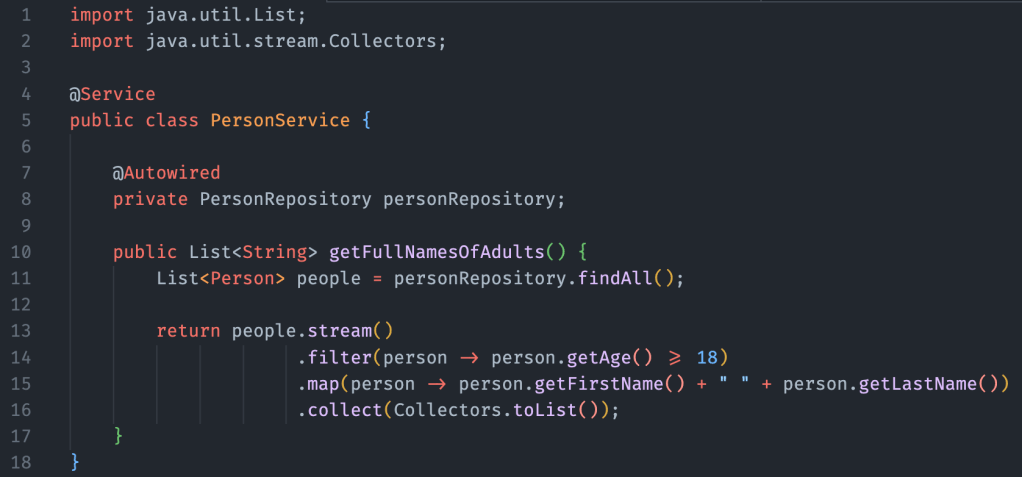
- Filtering and Mapping:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
public List<String> getFullNamesOfAdults() {
List<Person> people = personRepository.findAll();
return people.stream()
.filter(person -> person.getAge() >= 18)
.map(person -> person.getFirstName() + " " + person.getLastName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
In this example, we use a stream to filter adults from a list of Person entities, create full names by combining first and last names, and collect the results in a new list.
- Calculating Average Age:
import java.util.OptionalDouble;
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
public OptionalDouble calculateAverageAge() {
List<Person> people = personRepository.findAll();
return people.stream()
.mapToInt(Person::getAge)
.average();
}
}
Here, we use a stream to calculate the average age of all people stored in the database.
- Grouping by City:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
public Map<String, List<Person>> groupPeopleByCity() {
List<Person> people = personRepository.findAll();
return people.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getCity));
}
}
In this example, we use a stream to group Person entities by their city of residence and create a map with city names as keys and lists of people as values.
Final Note!
In this post, we explored the powerful combination of Java Streams and JPA for efficient and expressive data processing in Java applications. By leveraging the power of functional programming with Java Streams and the convenience of JPA, we can create elegant and efficient solutions for processing and manipulating relational data.
Let’s continue to explore related topics like advanced JPA features, querydsl, and other functional programming techniques in Java. Together, we’ll continue to learn, grow, and create a future brimming with endless possibilities in the world of software development!
📚 Further Reading & Related Topics
If you’re interested in optimizing data processing with Java Streams and JPA, these related articles will provide additional insights:
• Java Streams: Unleashing the Power of Functional Programming – Explore the fundamentals of Java Streams and how they enhance functional programming in Java applications.
• Mastering Dependency Management with Maven – Learn how to efficiently manage dependencies in your Java projects, ensuring seamless integration of JPA and other persistence tools.








Leave a comment